How To Calculate Earnings Per Share On Income Statement (step-by-step Guide)

Ever found yourself staring at a company's financial report, wondering what all those numbers really mean? You're not alone! It's like trying to decipher a secret code, right? But what if I told you there's one little metric that can give you a surprisingly clear picture of a company's profitability, all without needing a business degree? Yep, we're talking about Earnings Per Share, or EPS for short. It might sound a bit technical, but trust me, it's a pretty cool concept once you break it down.
Think of it this way: Imagine you're at a pizza party, and there are a bunch of slices. EPS is basically saying, "How much of that delicious pizza profit does each slice (or share) of ownership get?" Pretty neat, huh? It’s a way to size up how well a company is doing for its owners, which is a pretty fundamental question for anyone interested in investing or just understanding the business world better.
So, how do we actually find this magical EPS number? Don't worry, we're not going to get lost in a jungle of spreadsheets. We're going to take a chill, step-by-step journey, armed with our trusty income statement. What's an income statement, you ask? It's basically a report card for a company's financial performance over a specific period, showing its revenues, expenses, and ultimately, its profit. Think of it as the company's score for the semester.
Unpacking the Income Statement: Your EPS Treasure Map
Alright, first things first, you need access to a company's income statement. Most public companies make these readily available. You can usually find them on their investor relations website or through financial news sites. Once you've got it open, we're looking for two main things. It's like finding the ingredients for our EPS recipe.
The first ingredient is the company's net income. This is usually the very last line on the income statement, the bottom line, the grand total of what's left after all the bills are paid. If a company is making money, this number will be positive. If it's having a tough time, it might be negative (which is still important information, mind you!).
Think of net income as the total amount of delicious cookie dough the bakery made after buying all the flour, sugar, and chocolate chips, and paying the bakers. It's the total profit before we even think about who gets a piece.
The Second Ingredient: Shares, Glorious Shares!
Now for the second crucial piece of the puzzle: the number of outstanding shares. This refers to the total number of a company's shares that are currently held by all its shareholders. This information isn't always directly on the main income statement itself. You might have to dig a little deeper, perhaps in the notes section of the financial report or on a separate company profile page. But it's essential!
Why is this important? Because the more shares a company has, the thinner that net income pie gets divided. If a company has a huge profit but also a gazillion shares out there, each share might only get a tiny sliver of that profit. Conversely, a company with fewer shares and a decent profit can have a much higher EPS.
Imagine our cookie dough again. If you're sharing it among 5 friends, everyone gets a pretty big chunk. If you're sharing it among 50 friends, well, you get the idea. The number of shares is like the number of friends at the cookie party.
Calculating Basic EPS: The Straightforward Approach
Okay, ready for the main event? Calculating Basic Earnings Per Share is wonderfully straightforward. You simply take your net income (that bottom line number) and divide it by the total number of outstanding shares.
The formula looks like this:
Basic EPS = Net Income / Number of Outstanding Shares
Let's say a company reports a net income of $10 million. And it has 5 million shares outstanding. Your calculation would be: $10,000,000 / 5,000,000 = $2.00 per share.
So, for every share of this company you own, you're essentially entitled to $2.00 of its profits for that period. Pretty clear, right? It's like saying, "For every dollar I invested in this company's stock, I got $2 back in profit!" Well, not exactly, but you get the idea of how it reflects profitability per share.

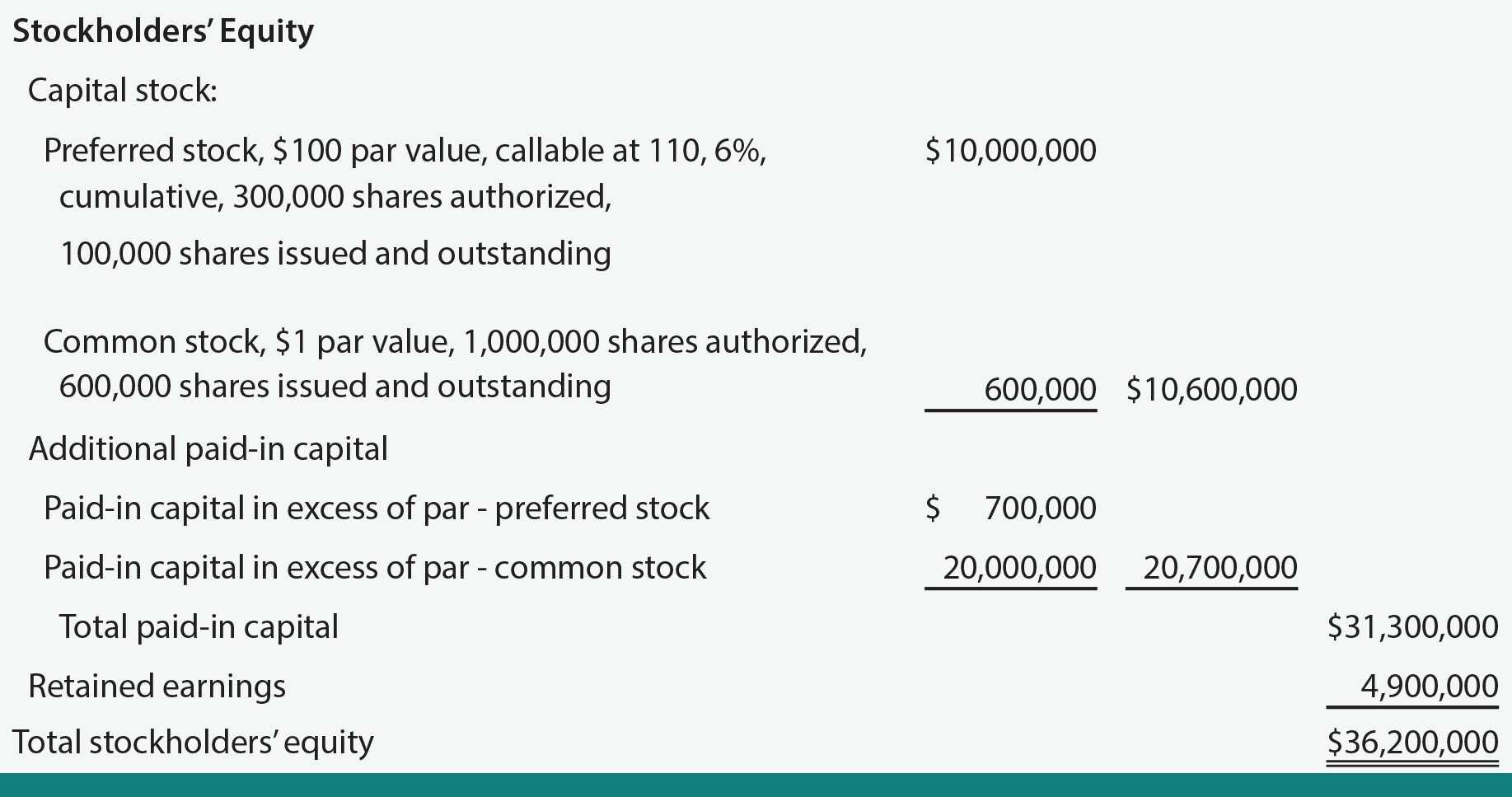
A Tiny Complication: Preferred Dividends
Now, before we get too comfortable, there's a little wrinkle to consider, especially for companies that have different classes of stock. We're talking about preferred dividends. Preferred shareholders usually have a fixed dividend they receive before common shareholders get anything. Think of them as the VIP guests who get their special appetizer first.
If a company pays out preferred dividends, you need to subtract that amount from the net income before you divide by the number of shares. This ensures that the EPS calculation only reflects the profit available to the common shareholders.
So, the formula for Basic EPS, when preferred dividends are involved, becomes:
Basic EPS = (Net Income - Preferred Dividends) / Number of Outstanding Shares
Let's say our company still made $10 million in net income, but it had to pay out $1 million in preferred dividends. And it still has 5 million shares outstanding. The calculation would be: ($10,000,000 - $1,000,000) / 5,000,000 = $9,000,000 / 5,000,000 = $1.80 per share.

See how that $0.20 difference per share matters? It's all about being precise and understanding who gets what slice of the profit pie.
Diluted EPS: The "What If" Scenario
Now, let's step into the realm of "what if?" This is where Diluted Earnings Per Share comes in. Why "diluted"? Because certain financial instruments can potentially turn into common shares in the future, "diluting" the ownership of existing shareholders. These are things like stock options, warrants, or convertible bonds.
Imagine a company has the option to issue more shares later. Diluted EPS tries to account for that possibility, giving you a more conservative view of profitability per share. It's like planning for a potentially larger party – you want to make sure you have enough pizza for everyone, even the guests who might show up.
Calculating diluted EPS is a bit more complex, as it involves figuring out how many new shares could be issued and how that would affect the earnings. Companies have specific accounting rules to follow for this, but the general idea is to include the impact of these potential shares in the calculation.
The formula for Diluted EPS generally looks like:
Diluted EPS = (Net Income - Preferred Dividends) / (Weighted Average Number of Outstanding Common Shares + Potential Common Shares from Dilutive Securities)

The "weighted average" part is because the number of outstanding shares can change throughout the reporting period. It's a way to smooth things out. And "potential common shares from dilutive securities" is the catch-all for those options, warrants, and convertible bonds.
Why bother with diluted EPS? Because it gives you a more complete picture of potential future earnings dilution. It’s a more cautious approach and can be a great indicator for investors watching for potential future earnings pressure.
Why Should You Care About EPS?
So, we've walked through the steps, but why is this whole EPS thing worth your brainpower? Well, EPS is like a company's performance review. A growing EPS often suggests a company is becoming more profitable, which is generally a good sign for its owners.
Investors use EPS to compare the profitability of different companies, even if they are different sizes. It's a standardized metric, like comparing apples to apples (or rather, profit slices to profit slices).
It also helps in evaluating a company's stock. Many stock prices are often related to their EPS through ratios like the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio. A higher EPS can sometimes justify a higher stock price, assuming everything else is equal. Think of it as a company's "value" relative to how much profit it's generating per share.
Ultimately, understanding EPS empowers you. It's a key piece of information that can help you make more informed decisions, whether you're thinking about investing a little nest egg or just trying to understand the financial health of businesses around you. So, the next time you see an income statement, you'll know exactly where to look for that sweet, sweet EPS number!
