Radiology Tech School Faq: Timelines, Clinical Hours, And Licensing
So, you're thinking about becoming a radiology technologist? Awesome choice! It's a career that's kinda like being a medical detective, using cool tech to peek inside the human body and help doctors figure out what's going on. But before you dive headfirst into the world of X-rays and CT scans, you probably have a bunch of questions. Totally normal! It’s like planning a road trip – you want to know how long it'll take, what you’ll need to pack, and what the final destination looks like, right? Well, let's unpack some of the most common questions about radiology tech school, focusing on the nitty-gritty like timelines, clinical hours, and licensing. Think of this as your friendly, no-stress guide.
The Big Picture: How Long Does This Thing Take?
This is often the first thing on everyone's mind. How long will you be hitting the books and the labs? Generally, you're looking at a couple of main paths: an associate's degree and a bachelor's degree.
Associate's Degree (The Speedy Gonzales Route)
The associate's degree is usually a two-year program. It’s a fantastic option if you’re eager to get into the field relatively quickly. It’s like choosing a zippy scooter for a city commute – efficient and gets you where you need to go without too much fuss. These programs give you a solid foundation in the core concepts of radiology, the technology involved, and patient care. You'll learn the ins and outs of operating X-ray machines, understanding different imaging procedures, and making sure your patients are comfortable and safe.
Bachelor's Degree (The Deep Dive)
A bachelor's degree will typically take four years. This route is more like opting for a sturdy, reliable SUV for a cross-country adventure. It gives you a more in-depth understanding of the science behind medical imaging, broader healthcare concepts, and sometimes even a specialization. If you're interested in areas like research, management, or teaching down the line, a bachelor's might be your jam. It opens up a lot of doors for advanced roles and opportunities.
Keep in mind that these are general timelines. Factors like whether you're attending full-time or part-time, any prerequisite courses you might need to complete beforehand, and the specific structure of the program at your chosen school can all play a role. So, always check with the schools you're interested in for their exact program lengths!

The Real Deal: Clinical Hours – What Are They and Why Do They Matter?
Alright, let's talk about clinical hours. This is where the rubber meets the road, or rather, where the X-ray beam meets the patient (safely, of course!). Clinical hours are essentially your hands-on training in a real hospital or imaging center. You're not just reading about how to position a patient for an X-ray; you're actually doing it under the supervision of experienced professionals. Think of it like learning to ride a bike. You can read all the books you want, but you won't truly learn until you get on and start pedaling, with someone holding onto the back to make sure you don't tumble!
Why Are They So Important?
Clinical hours are crucial for several reasons. First, they're where you gain practical skills. You'll learn how to operate the equipment, interact with patients from all walks of life, handle different scenarios, and understand the workflow of an imaging department. It's about building confidence and competence.
Second, they give you a real-world perspective. Textbooks can only teach you so much. Being in a clinical setting exposes you to the day-to-day realities of the job, the pace of work, and the importance of teamwork. You’ll see firsthand how your skills contribute to patient care and diagnosis.
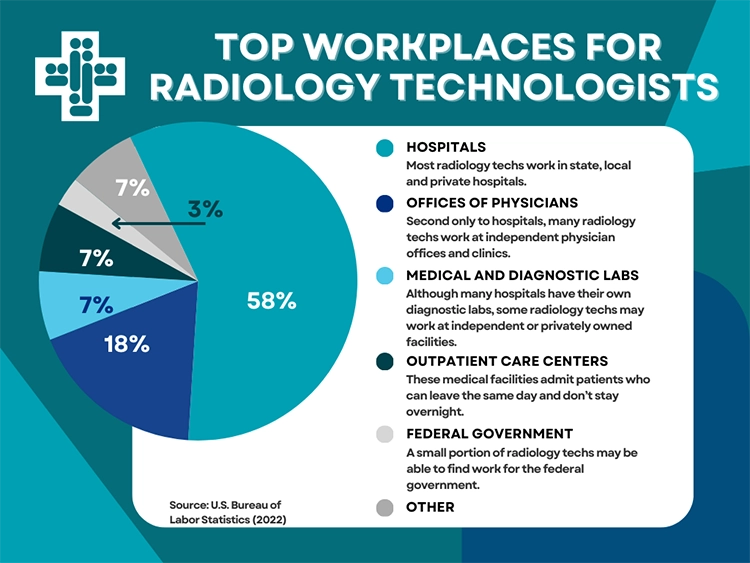
How Many Hours Are We Talking About?
The number of required clinical hours can vary significantly depending on the program and the credentialing body. However, you can generally expect to dedicate a substantial amount of time to your clinical rotations. For an associate's degree program, you might be looking at somewhere between 1,200 to 1,800 clinical hours. For a bachelor's, it could be even more. These hours are typically spread out over a year or two of your program, often in blocks of several days a week.
It's not just about showing up; it's about actively participating, observing, and learning. You'll be mentored by seasoned technologists who will guide you, correct you, and cheer you on. It’s an incredibly valuable part of your education, and many students find it to be the most rewarding. You might even discover what specific areas of radiology you enjoy the most!
The Golden Ticket: Licensing and Certification – What's the Deal?
So, you've aced your classes, rocked your clinicals, and graduated. Now what? The next step to becoming a practicing radiology technologist is usually licensing and/or certification. This is like getting your driver's license – it’s the official stamp of approval that says you’re qualified to do the job safely and effectively.

Why Is Licensing Necessary?
Licensing is primarily about public safety. It ensures that only individuals who have met specific educational and competency standards are allowed to practice. Different states have different licensing requirements, so it's essential to research the regulations in the state where you plan to work.
The National Standard: Certification
While licensing is often state-specific, certification is usually a national standard. The most common and respected certification for radiology technologists in the U.S. is offered by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). To become an ARRT-certified radiographer, you’ll need to pass a comprehensive exam that covers a wide range of topics related to the profession.
Think of the ARRT exam as the ultimate pop quiz on everything you've learned. Passing it is a huge accomplishment and a major step toward your career. Many employers will require you to be certified, and in some states, passing the ARRT exam is part of the licensing process.
What About Other Specializations?
Radiology is a big field, and you might want to specialize in areas like CT scanning, MRI, mammography, or nuclear medicine. The ARRT offers separate certifications for these specializations, which can significantly boost your career prospects and earning potential. It’s like getting a special badge after you’ve mastered a particular skill!
The process for obtaining these certifications and licenses usually involves graduating from an accredited program, meeting specific prerequisite coursework or clinical hour requirements, and passing the relevant exams. It might sound like a lot, but remember, your school will guide you through this process. They know the drill!
Putting It All Together
Navigating the path to becoming a radiology technologist can seem a bit daunting at first with all the different steps and requirements. But break it down, and it’s totally manageable! You're looking at programs that are typically two to four years long, a significant chunk of which will be spent gaining invaluable hands-on clinical experience, and finally, obtaining your license and/or certification to officially join the ranks. It’s a journey that requires dedication and hard work, but the reward is a fulfilling career where you make a real difference in people's lives every single day. Pretty cool, huh?
